India has made rapid advances in economic growth, with our per capita GDP growing 7.5X from $300 in 1991 to $2250 in 2021. Basis our demographic dividend, continued investments in innovation and technical adoption across the spectrum, India is poised to be the 3rd largest economy by 2031.
Basis historical anecdotal data, the process of economic growth has always been accompanied by even faster growth in global trade. India's exports and share of Global Trade will significantly play a significant role in the next growth phase of the Indian economy.
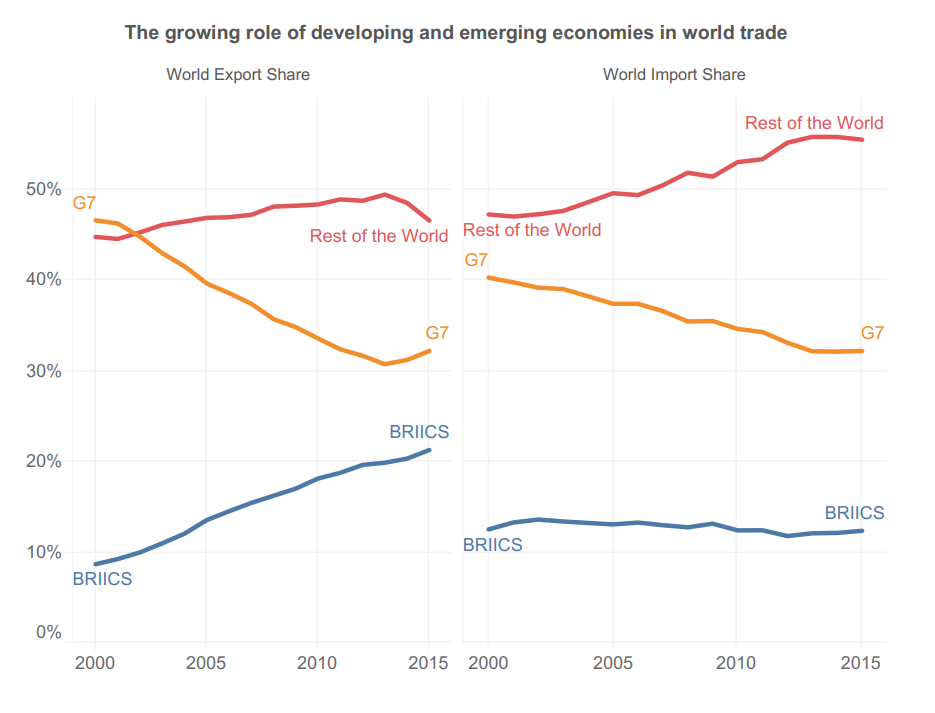
As per WTO data, India exported goods worth $670 billion (Rs 50 lakh crore) and its merchandise exports were at a record $418 billion. There is potential for this to grow to $2T by 2030, at a growth of 15-20%. Today, India’s share in global exports for merchandise is <2% and in global imports <3%. China's share of global trade is in excess of 15% - and all this growth has come about in the last 30 years starting from a similar baseline
There is one clear takeaway for the entire ecosystem - International trade from and to India is expected to boom, and consequently enablers of commerce - across goods and services and across Large, Medium and MSME business will grow manifold as the global economy opens up.
It is important to note that there are several use cases for cross border payments – Remittances ($900B-$1000B, with an average cost of 3-6% comprising Banks, MTO’s, MMO’s and Fintechs); Large B2B payments which include government purchases for crude etc which is in excess of $150T (with an average pricing of 10bps and managed largely by Global Banks and their Trade and Treasury departments). The focus of this document is to understand the relevant commerce ecosystem related flows (B2C and C2B; which are in excess of $3T combined globally; with an average cost of 2.5-4%)

Defining the size of the prize
As of FY21; there was a $100B addressable market in India to facilitate Imports and Exports
- Indian Exports $643B with Goods $402B and Services $241B
- Removing large Industrial goods and IT flows - $150B
- Removing Gems & Jewellery and other Agri flows - $60B
- Indian Imports $717B with Goods ($580B) and Services $137B
- Removing large flows - $153B
- Removing Gems & Jewellery and other Agri flows - $30B
In India, Export and Import trade is promoted and facilitated by the Directorate General of Foreign Trade (DGFT), under the Ministry of Commerce and Industry (MoCI). The DGFT also implements the Foreign Trade Policy of India which is the prime policy that lays down simple and transparent procedures for efficient management of foreign trade in India.
In India, RBI overseas the management of foreign exchange and purpose for inward and outward remittances through Foreign Exchange Management Act. It lays down the ground rules for various participants (AD1 Banks, MTSS operators) including licensing them. To promote specific areas of trade the RBI also facilitates programs such as processing and settlement of import and export related payments facilitated by Online Payment Gateway Service Providers (OPGSP), Rupee Drawing arrangement, Liberalized Remittance Scheme etc.
Impact on Business and Economy:
Efficient cross-border payment systems have a direct impact on businesses and the overall economy. For businesses, streamlined cross-border transactions reduce costs, improve cash flow, and enable faster access to international markets. According to a survey conducted by HSBC, 79% of Indian businesses believe that improving cross-border payments positively impacts their competitiveness. Additionally, seamless cross-border payment channels contribute to attracting foreign investments and fostering economic growth.
While most of these payments are being serviced by AD1 Banks in the country today, there are challenges faced in the ecosystem
- Economics (Risk vs Reward, Profit center vs Enabler, fully loaded pricing)'
- Regulations & Jurisdiction (Inbound/Outbound corridors, Data reporting requirements, Permitted entities and nature of trade)
- Payment methods (Availability, Completion, Trust, Price including FX)
- Timing (Goods vs Services, subscriptions, services rendered via prepaid, postpaid mechanisms)
- Trust (Insurance - Buyer/Seller protection, AML, ATF, SDN lists)
Cross-border payments in India have witnessed significant advancements driven by technology, regulatory reforms, and innovative solutions. The country's commitment to digital transformation, and growing global trade, emphasizes the importance of efficient and secure cross-border payment systems. As India continues to evolve as a major player in the global economy, it is crucial to prioritize the development of comprehensive, accessible, and future-ready cross-border payment infrastructure to facilitate seamless international transactions.
We will continue to explore how the Fintech ecosystem is solving for these challenges and what lies ahead in the future for merchants, consumers and regulations in future versions of the blog.